In recent years, the concept of CO2 tolerance has gained attention for its role in reducing anxiety, improving physical performance, and optimising overall health. Understanding how carbon dioxide (CO2) functions within the body can empower you to enhance your breath control, regulate your nervous system, and achieve greater physical and mental resilience. This article is a must-read for anyone looking to improve their CO2 tolerance, whether you’re an athlete, someone managing stress, or simply interested in the science of respiration.
Article Outline
- What is CO2 Tolerance?
- Why Is CO2 Tolerance Important?
- How Does CO2 Influence the Body?
- The Role of Breath Control in CO2 Tolerance
- Breath-Holding and CO2 Tolerance: What You Need to Know
- The Benefits of CO2 Tolerance for Athletes
- Breathing Exercises to Improve CO2 Tolerance
- How CO2 Tolerance Can Help Reduce Anxiety
- Nasal Breathing vs. Mouth Breathing
- Common Misconceptions About CO2
1. What is CO2 Tolerance?
CO2 tolerance refers to the body’s ability to tolerate higher levels of carbon dioxide without triggering the urge to breathe excessively. Contrary to popular belief, carbon dioxide is not just a waste product; it plays a crucial role in your respiratory system, impacting how oxygen is released to your muscles and organs. This physiological process, known as the Bohr Effect, highlights the importance of CO2 in maintaining efficient oxygen delivery and overall health.
When you increase CO2 tolerance, your body becomes more efficient at utilising oxygen, leading to improved physical performance and a calmer nervous system. Understanding CO2 tolerance is essential for anyone looking to optimise their breathing patterns and enhance their physiological resilience.
2. Why Is CO2 Tolerance Important?
CO2 tolerance is critical for both physical and mental well-being. Physically, a higher tolerance to carbon dioxide allows for better oxygen delivery during exercise, improving endurance and athletic performance. Mentally, increasing CO2 tolerance can reduce anxiety by stabilising the nervous system, making it easier to manage stress and maintain focus.
By improving your CO2 tolerance, you can enhance your body’s ability to perform under pressure, whether you’re a runner, a swimmer, a surfer, a track athlete, a soccer player, a weekend warrior or simply navigating daily stressors. The benefits of CO2 tolerance extend beyond the physical realm, offering significant advantages for mental clarity and emotional stability.
3. How Does CO2 Influence the Body?
Carbon dioxide is a key player in the body’s ability to deliver oxygen to tissues, thanks to the Bohr Effect. When CO2 levels are higher, oxygen is more readily released from the bloodstream to the muscles and organs, which is vital for maintaining energy and reducing fatigue. This process also helps regulate blood pH, preventing respiratory alkalosis—a condition that occurs when CO2 levels drop too low, leading to symptoms like dizziness, anxiety, and decreased physical performance.
The body’s ability to tolerate higher levels of carbon dioxide is directly linked to improved oxygen delivery, which in turn supports better physiological function and overall health.
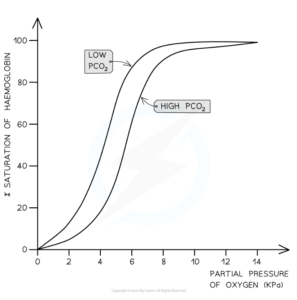
The above diagram shows how hemoglobin’s affinity for oxygen decreases in response to increased levels of carbon dioxide and decreased pH, making oxygen release more efficient in active tissues. This phenomenon, known as The Bohr Effect, is crucial for understanding oxygen transport in the body, especially during exercise or at high altitudes. Image courtesy of Save My Exams.
4. The Role of Breath Control in CO2 Tolerance
Breath control plays a pivotal role in CO2 tolerance. The way you breathe—whether it’s shallow or deep, fast or slow—affects the amount of CO2 retained in your blood. Controlled, rhythmic breathing can help increase CO2 tolerance by ensuring that carbon dioxide levels remain balanced, optimising oxygen delivery to the body.
Breathing techniques which emphasise the importance of gentle, nasal breathing maintain higher CO2 levels and reduce the urge to over-breathe. By practicing proper breath control, you can improve your body’s ability to tolerate higher CO2 levels, leading to better physical and mental outcomes.
5. Breath-Holding and CO2 Tolerance: What You Need to Know
Breath-holding is a powerful tool for improving CO2 tolerance. When you hold your breath, CO2 levels naturally rise, training your body to tolerate higher concentrations of carbon dioxide. This practice can enhance your physical performance by increasing your body’s efficiency in using oxygen, especially during strenuous activities.
However, it’s important to approach breath-holding exercises with caution. Start by gradually increasing the duration of your breath holds, ensuring that you’re doing so in a safe and controlled environment. Over time, you’ll notice a significant improvement in your ability to manage CO2 levels and maintain calm under pressure.
6. The Benefits of CO2 Tolerance for Athletes
For athletes, CO2 tolerance is a game-changer. Higher CO2 tolerance allows for more efficient oxygen delivery, which is crucial for sustaining physical performance during long and intense workouts. This increased efficiency can lead to a higher VO2 max, which measures the maximum amount of oxygen your body can utilise during exercise.
Athletes who focus on improving their CO2 tolerance often experience enhanced endurance, faster recovery times, and better overall performance. By incorporating CO2 tolerance training into your regimen, you can unlock new levels of athletic potential and reach your fitness goals more effectively.
7. Breathing Exercises to Improve CO2 Tolerance
There are several effective breathing exercises that can help improve CO2 tolerance. The Buteyko method, for example, involves inhaling through the nose and exhaling gently and slowly, allowing CO2 to accumulate in the body and increase tolerance. Box breathing is another technique that promotes CO2 tolerance by encouraging slow, controlled breaths in a rhythmic pattern. I am a fan of nasal breathing with a 4-5 second inhale and a 8-10 second exhale, imagining you have a feather placed directly in front of your nostrils and aiming not to disturb the feather!
To incorporate these breathing exercises into your routine, start with short, daily sessions, gradually increasing the duration as your tolerance improves. Over time, you’ll notice a significant boost in your ability to manage CO2 levels and maintain a calm, focused state.
8. How CO2 Tolerance Can Help Reduce Anxiety
CO2 tolerance is closely linked to the body’s stress response. When CO2 levels are low, the body is more prone to anxiety and stress sensitivity. Remember that old-time advice to breathe into a paper bag when feeling anxious? By improving your CO2 tolerance, you can reduce anxiety and promote a calmer, more relaxed state of mind.
Breathing techniques that emphasise slow, controlled exhales can help maintain higher CO2 levels, stabilising the nervous system and reducing the physical symptoms of anxiety. This connection between CO2 tolerance and mental health makes it a valuable tool for anyone looking to manage stress more effectively.
9. Nasal Breathing vs. Mouth Breathing
Nasal breathing is generally superior to mouth breathing when it comes to CO2 tolerance. Breathing through your nose helps maintain higher levels of CO2 in the blood, which is essential for efficient oxygen delivery and overall respiratory health. Nasal breathing also promotes proper ventilation and prevents hyperventilation, a common issue associated with mouth breathing.
Transitioning to nasal breathing can take time, but the benefits are well worth the effort. By making this switch, you can improve your CO2 tolerance, enhance your physical performance, and support better overall health.
Try taping your mouth at night (vertically rather than horizontally) with a surgical tape. You may wake up feeling surprisingly refreshed.
10. Common Misconceptions About CO2
CO2 often gets a bad rap, but it’s essential for maintaining optimal physiological function. While it’s true that excess CO2 can be harmful, the right amount is crucial for oxygen delivery and energy production. Many people mistakenly believe that deep, rapid breathing will increase oxygen levels in the body, but this can actually lower CO2 levels and reduce oxygen availability.
Understanding the role of CO2 in the body is key to optimising your respiratory health. By debunking common myths and embracing the benefits of CO2 tolerance, you can improve your breathing patterns, reduce anxiety, and enhance your overall well-being.
Summary: Key Takeaways
- CO2 tolerance is crucial for both physical and mental health, influencing how well oxygen is delivered to your tissues.
- Breath control is essential for maintaining proper CO2 levels, which support optimal physiological function.
- Breath-holding exercises can help increase CO2 tolerance, but should be practiced safely and gradually.
- Athletes benefit greatly from higher CO2 tolerance, which improves endurance and performance.
- Breathing exercises like the Buteyko method and box breathing can enhance CO2 tolerance over time.
- Reducing anxiety is another significant benefit of improved CO2 tolerance, as it stabilises the nervous system.
- Nasal breathing is superior to mouth breathing for maintaining healthy CO2 levels and preventing hyperventilation.
